Featured Publications
For the full list, see Google Scholar
2025
22. Precise Control of C = C Bonds in Polyisoprene (PI)–Containing Block Copolymers via Diimide Hydrogenation
Luis Felipe Caspari Thiele, Yongha Kim, Corey Roberts, Andrew Zydney, Ralph Colby, Manish Kelkar, Uwe Beuscher, and Hee Jeung Oh*. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2025, Under Revision
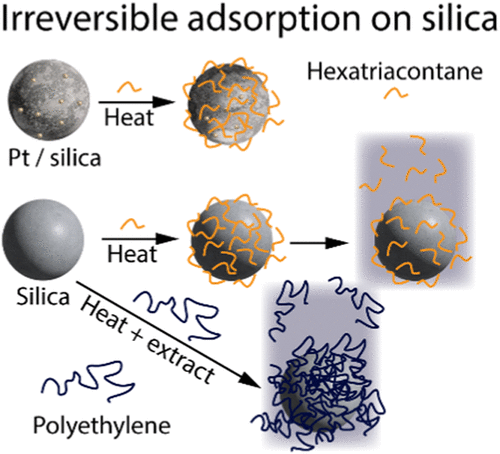
21. Hydrocarbon Deposition during Polyolefin Upcycling: Irreversible Adsorption and Surface Reactions of Polyethylene and Ethylene Oligomers on Silica Supports
Fawaz Motolani, Rebekah Snellings, Sogand Aghamohammadi Ghandilou, Hee Jeung Oh, Gina Noh, Bert Chandler, and Bryan Vogt. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research (I&ECR), 2025, 64, 12, 6475–6486
Catalytic conversion of polyolefins to value-added products offers an alternative route to capture value from plastic waste. The results demonstrate significant, nonextractable hydrocarbon deposition on catalyst support surfaces without dehydrogenation catalyst present at temperatures typical of catalytic deconstruction of polyolefin waste, which may limit catalyst turnover and impact the product distribution.
20. Detergent/Surfactant Retention during Ultrafiltration in the Formulation of Biotherapeutics
Liang-Kai Chu, Zhuoshi Du, Matthew Billups, Hee Jeung Oh, and Andrew L. Zydney. Biotechnology Progress, 2025, 41, 3, e70011
Surfactants like polysorbate (Tween®) are commonly used as excipients in the production of monoclonal antibodies and other recombinant proteins. A simple mathematical model was developed to describe the polysorbate transmission accounting for the effects of concentration polarization as well as the presence of surfactant monomers and micelles.
2024
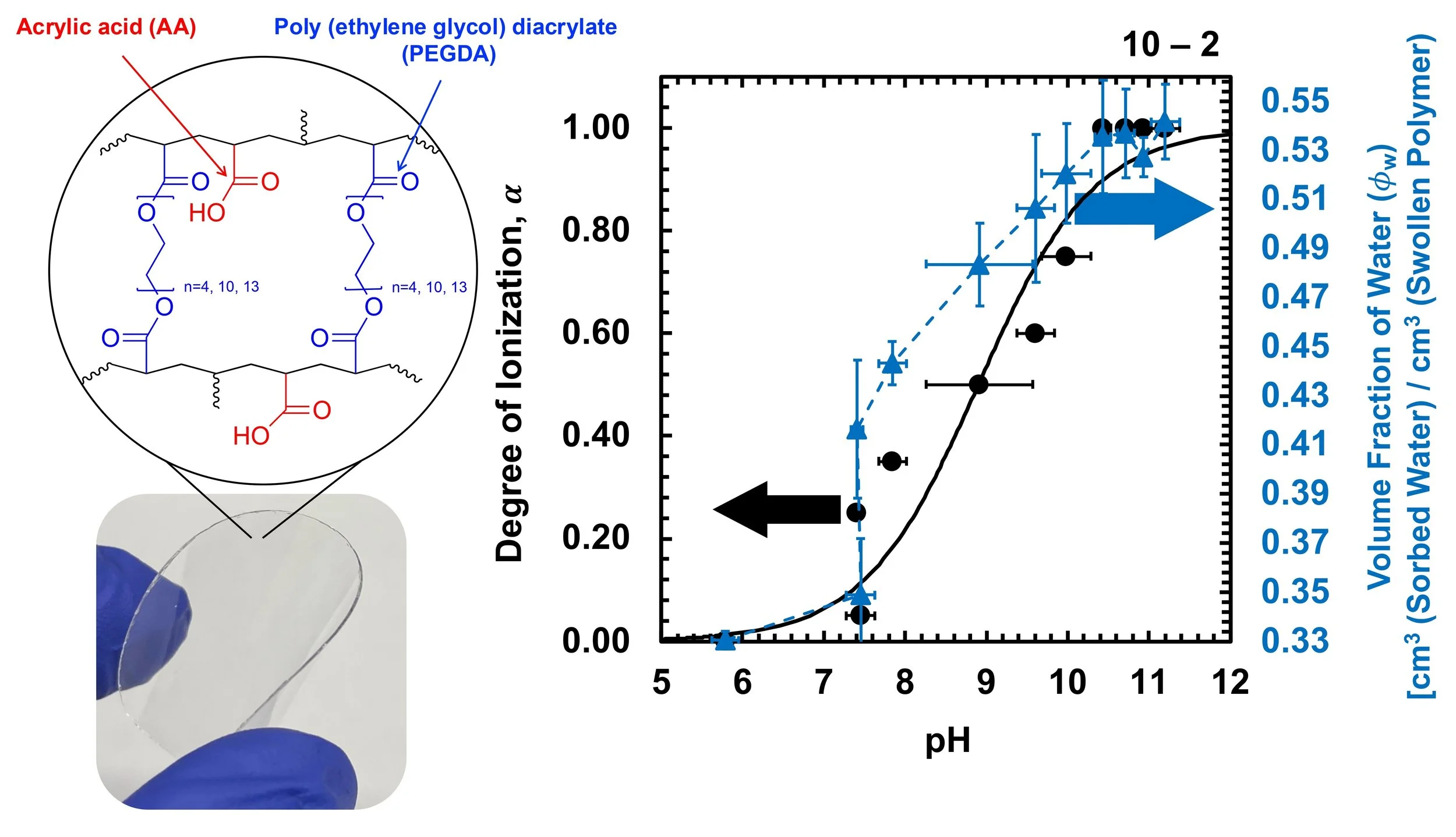
19. Determination of Carboxyl Dissociation Degree and pKa in Weak Polyelectrolyte Membranes via POT Titration and FTIR Analysis for Clean Technologies in Sustainability
Yongha Kim, Taekwon Kim, Dae Eun Kang, Jack S. Szymanski, Riley B. Kracaw, Andrew J. Lukaszewski, Kyle M. Tierney, Michael A. Shaqfeh, Charleen M. Rahman and Hee Jeung Oh*. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 22, 10844–10860
Highlighted in Journal Cover
To systematically quantify the dissociated charged group content in the polymers, we reported the degree of ionization (α) and negative logarithm of acid dissociation constant (pKa) of AA-PEGDA series at varied external pH via conventional potentiometric titration (POT titration) and widely available ATR-FTIR analysis. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time the charged group concentration (mIEC) and cross-linking density have been systematically changed to record the pKa trend in thin film forms using a single polymer network system.
18. Weak Polyelectrolyte Membranes with a Wide Ion-Exchange Capacity (IEC) Range and Limited Water Swelling in Clean Technologies for Sustainability
Yongha Kim, Taekwon Kim, Dae Eun Kang, Riley B. Kracaw, Andrew J. Lukaszewski, Jack S. Szymanski, Charleen M. Rahman, Michael A. Shaqfeh, Kyle M. Tierney, Hai Doan, Lauren Collins, and Hee Jeung Oh*. ACS Applied Polymer Materials 2024, 6, 18, 11334–11349
Charged polymer membranes are of great interest in clean technologies for sustainability. In this context, we have designed a systematic library of weak polyelectrolyte membranes: cross-linked acrylic acid–poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (AA-PEGDA) networks, with a wide range of ion-exchange capacity (IEC = 0–4 mequiv/g) and limited water swelling. This AA-PEGDA series can provide extra freedom to modify transport properties via simply changing the pH and enable us to develop a mechanistic understanding of water and ion transport in charged polymer membranes.
17. Polymer Physics of Separation Membranes
Hee Jeung Oh* and William A. Phillip*, Macromolecules 2024, 57, 20, 9489–9497
Co-Editor of Macromolecules and ACS Macro Letters’ Collection “Polymer Physics of Separation Membranes”
Membrane-based separations have the potential to help address a broad array of grand technical challenges. A key theme is the integration of techniques that probe the molecular-scale phenomena including scattering and spectroscopy with practical measurements of membrane performance. This interdisciplinary approach, bridging polymer physics and membrane science, offers a pathway to innovate from the molecular to process scale.
2021
16. Heterogeneous Photoredox Catalysis using Fluorescein Polymer Brush Functionalized Glass Beads
Kirsten Bell, Sarah Freeburne, Michele Fromel, Hee Jeung Oh, and Christian W. Pester Journal of Polymer Science, 2021, 59, 2844-2853
Photocatalysis is a valuable and versatile method to perform a variety of chemical transformations under ambient temperatures and pressures using mild visible light. This work showcases an example of fluorescein-functionalized polymers grafted to micro-scale glass beads as heterogeneous photoredox catalysts.
2019
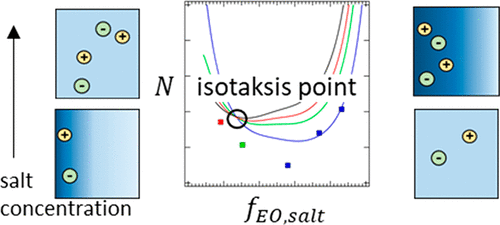
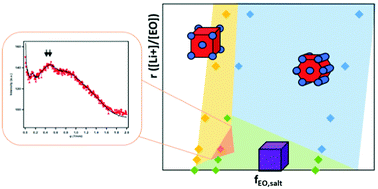
15. Composition Dependence of the Flory–Huggins Interaction Parameters of Block Copolymer Electrolytes and the Isotaksis Point
Whitney S. Loo, Gurmukh K. Sethi, Alexander A. Teran, Michael D. Galluzzo, Jacqueline A. Maslyn, Hee Jeung Oh, Katrina I. Mongcopa, and Nitash P. Balsara*, Macromolecules 2019, 52, 15, 5590–5601
The thermodynamics of block copolymer/salt mixtures were quantified through the application of Leibler’s random phase approximation to disordered small-angle X-ray scattering profiles. The experimental system is comprised of polystyrene-block-poly(ethylene oxide) (SEO) mixed with lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide salt (LiTFSI), SEO/LiTFSI. The Flory–Huggins interaction parameter determined from scattering experiments, χSC, was found to be a function of block copolymer composition, chain length, and temperature for both salt-free and salty systems.
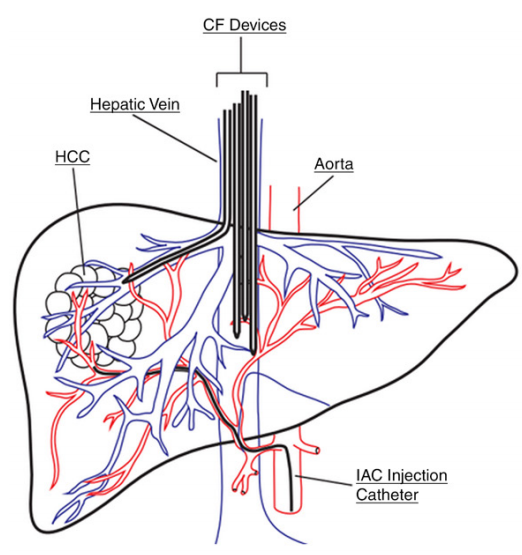
14. Endovascular Ion Exchange Chemofiltration Device Reduces Off-Target Doxorubicin Exposure in a Hepatic Intra-arterial Chemotherapy Model
Colin Yee, David McCoy, Jay Yu, Aaron Losey, Caroline Jordan, Terilyn Moore, Carol Stillson, Hee Jeung Oh, Bridget Kilbride, Shuvo Roy, Anand Patel, Mark W. Wilson, Steven W. Hetts, Radiology: Imaging Cancer, 2019, 1(1): 3190009
To determine if endovascular chemofiltration with an ionic device (ChemoFilter [CF]) can be used to reduce systemic exposure and off-target biodistribution of doxorubicin (DOX) during hepatic intra-arterial chemotherapy (IAC) in a preclinical model.
13. 3D Printed Absorber for Capturing Chemotherapy Drugs before They Spread through the Body
Hee Jeung Oh, Mariam S. Aboian, Michael Y. J. Yi, Jacqueline A. Maslyn, Whitney S. Loo, Xi Jiang, Dilworth Y. Parkinson, Mark W. Wilson, Terilyn Moore, Colin R. Yee, Gregory R. Robbins, Florian M. Barth, Joseph M. DeSimone, Steven W. Hetts, and Nitash P. Balsara, ACS Central Science, 2019, 5, 5, 419-427
Highlighted in Journal Cover
Featured in >50 international news channels including BBC News, The Washington Times, Independent, The Chemical Engineer, ACS Axial, and Science News
Despite efforts to develop increasingly targeted and personalized cancer therapeutics, dosing of drugs in cancer chemotherapy is limited by systemic toxic side effects. We have designed, built, and deployed porous absorbers for capturing chemotherapy drugs from the bloodstream after these drugs have had their effect on a tumor, but before they are released into the body where they can cause hazardous side effects.
2018
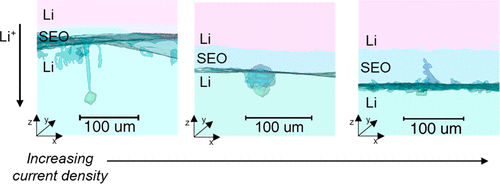
12. Growth of Lithium Dendrites and Globules through a Solid Block Copolymer Electrolyte as a Function of Current Density
Jacqueline A. Maslyn, Whitney S. Loo, Kyle D. McEntush, Hee Jeung Oh, Katherine J. Harry, Dilworth Y. Parkinso, and Nitash P. Balsara, Journal of Physical Chemistry, Part C: Energy Conversion and Processes, 2018, 122 (47), 26797-26804
The uncontrollable nonplanar electrodeposition of lithium is a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of high energy density rechargeable batteries with a lithium metal anode. A promising approach for preventing the growth of lithium dendrites is the use of solid polymer electrolytes with a high shear modulus.Our work enables comparisons between the experimentally determined onset of nonplanar electrodeposition and prevailing theoretical predictions with no adjustable parameters.
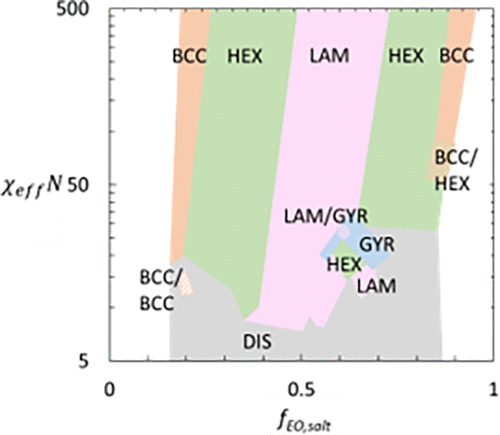
11. Phase Behavior of Mixtures of Block Copolymers and a Lithium Salt
Whitney S. Loo, Michael D. Galluzzo, Xiuhong Li, Jacqueline A. Maslyn, Hee Jeung Oh, Katrina I. Mongcopa, Chenhui Zhu, Andrew A. Wang, Xin Wang, Bruce A. Garetz, and Nitash P. Balsara, Journal of Physical Chemistry, Part B, 2018, 122 (33), 8065-8074
We present experimental results on the phase behavior of block copolymer/salt mixtures over a wide range of copolymer compositions, molecular weights, and salt concentrations. The phase behavior of salt-containing block copolymers, plotted on a segregation strength versus copolymer composition plot, is similar to that of conventional (uncharged) block copolymer melts, when the parameter χeff replaces χ in segregation strength.
10. Reentrant phase behavior and coexistence in asymmetric block copolymer electrolytes
Whitney S. Loo a, Xi Jiang b, Jacqueline A. Maslyn ab, Hee Jeung Oh a, Chenhui Zhu c, Kenneth H. Downing d and Nitash P. Balsara, Soft Matter, 2018, 14, 2789-2795
Highlighted in Journal Cover
In this work, we show that the addition of salt to a disordered asymmetric block copolymer first leads to the formation of coexisting ordered phases which give way to a reentrant disordered phase at a higher salt concentration. The coexisting phases are both body centered cubic (BCC) with different domain spacings, stabilized by partitioning of the salt.
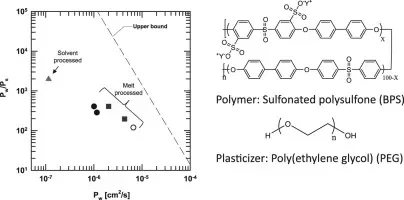
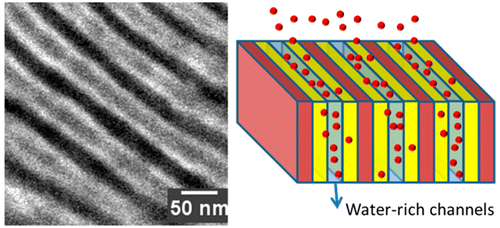
9. Water and Salt Transport Properties of Disulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone) Desalination Membranes Formed by Solvent-free Melt Extrusion
Hee Jeung Oh, James E. McGrath, and Donald R. Paul, Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 546, 234-245
This paper reports water and salt transport properties of sulfonated polysulfone desalination membranes prepared by solvent-free, melt extrusion. BPS-20K membranes prepared by different processing routes followed the trade-off relationship between water permeability and water/salt permeability selectivity. These results indicate that differences in membrane processing history have significant effects on the transport properties of small molecules in these polymers, similar to other glassy polymers.
2017
8. Kinetics of Poly(ethylene glycol) Extraction into Water from Plasticized Disulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone) Desalination Membranes Prepared by Solvent-free Melt Processing
Hee Jeung Oh, James E. McGrath, and Donald R. Paul, Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 524, 257-265
The rate of PEG extraction is affected by the molecular weight and concentration (wt%) of PEG in the extruded BPS-20K/PEG films, as well as the temperature. When the early time approximation and complete solution of a Fickian model were used to analyze the kinetic desorption of PEG materials from the extruded films, they were found to describe the data. The diffusion coefficients of the PEG materials determined from this analysis correlated well with temperature and follow the Arrhenius equation.
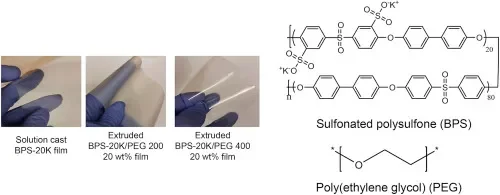
7. Formation of Disulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone) Thin Film Desalination Membranes Plasticized with Poly(ethylene glycol) by Solvent-free Melt Extrusion
Hee Jeung Oh, Jaesung Park, Sebnem Inceoglu, Irune Villaluenga, Jacob L. Thelen, Xi Jiang, James E. McGrath, and Donald R. Paul, Polymer, 2017, 109, 106-114
In this study, we discuss a new membrane formation route for preparing sulfonated polysulfone desalination membranes by solvent-free melt processing. Single-layer membranes composed of a 20 mol% disulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) random copolymer (BPS-20K) and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) plasticizers were successfully prepared by using melt extrusion.
2016
6. In vitro Clearance of Doxorubicin with a DNA-based Filtration Device Designed for Intravascular Use with Intra-arterial Chemotherapy
Mariam S. Aboian, Jay F. Yu, Ayushi Gautam, Chia-Hung Sze, Jeffrey K. Yang, Jonathan Chan, Prasheel V. Lillaney, Caroline D. Jordan, Hee-Jeung Oh, David M. Wilson, Anand S. Patel, Mark W. Wilson and Steven W. Hetts, Biomedical Microdevices, 2016, 18:98
To report a novel method using immobilized DNA within mesh to sequester drugs that have intrinsic DNA binding characteristics directly from flowing blood. A DNA-containing ChemoFilter device can rapidly clear clinical doses of doxorubicin from a flow model in simple and complex physiological solutions, thereby suggesting a novel approach to reduce the toxicity of DNA-binding drugs.
5. Block Copolymer Membranes for Efficient Capture of a Chemotherapy Drug
X. Chelsea Chen, Hee Jeung Oh, Jay F. Yu, Jeffrey K. Yang, Nikos Petzetakis, Anand S. Patel, Steven W. Hetts, and Nitash P. Balsara, ACS Macro Letters, 2016. 5(8), 936-941
Highlighted as ACS Editor’s Choice Article
We introduce the use of block copolymer membranes for an emerging application, “drug capture”. The polymer is incorporated in a new class of biomedical devices, referred to as ChemoFilter, which is an image-guided temporarily deployable endovascular device designed to increase the efficacy of chemotherapy-based cancer treatment.
2014
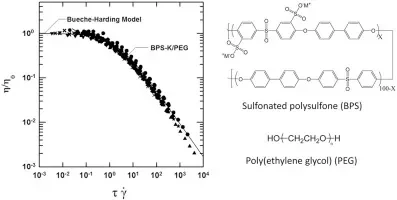
4. Rheological Studies of Disulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone) Plasticized with Poly(ethylene glycol) for Membrane Formation
Hee Jeung Oh, Benny D. Freeman, James E. McGrath, Christopher J. Ellison, Sue Mecham, Kwan-Soo Lee, and Donald R. Paul, Polymer, 2014. 55, 1574-1582
In this study, the rheological properties of disulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone)s plasticized with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) are investigated to identify coextrusion processing conditions with candidate PPs. The rheological data effectively lie on the same master curve developed by Bueche and Harding for non-associating polymers such as poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) and polystyrene (PS). Although sulfonated polysulfone contains ionic groups, the form of its viscosity versus shear rate (or frequency) behavior appears to be dominated by the relaxation of polymer entanglements.
3. Thermal Analysis of Disulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone) Plasticized with Poly(ethylene glycol) for Membrane Formation
Hee Jeung Oh, Benny D. Freeman, James E. McGrath, Chang Hyun Lee, and Donald R. Paul, Polymer, 2014, 55, 235-247
One route to melt processing of high glass transition temperature polyelectrolytes, such as disulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) (BPS), involves mixing a plasticizer with the polymer. In this study, poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) was used as a plasticizer for BPS. BPS and PEG are miscible, and the effect of PEG molecular weight (in the range of 200–600 g/mol) and concentration on the Tg of BPS/PEG blends was investigated.
2011
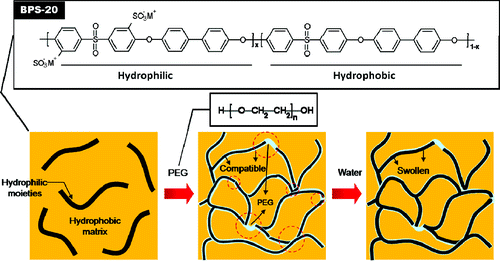
2. Disulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone) Random Copolymer Blends Tuned for Rapid Water Permeation via Cation Complexation with Poly(ethylene glycol) Oligomers
Chang Hyun Lee, Desmond VanHouten, Ozma Lane, James E. McGrath, Jianbo Hou, Louis A. Madsen, Justin Spano, Sungsool Wi, Joseph Cook, Wei Xie, Hee Jeung Oh, Geoffrey M. Geise, and Benny D. Freeman, Chemistry of Materials, 2011, 23(4), 1039-1049
We present fundamental studies of a new blending strategy for enhancing water permeability in ionomeric reverse osmosis membrane materials. A random disulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) copolymer containing 20 mol percent hydrophilic units (BPS-20) in the potassium salt (−SO3K) form was blended with hydroxyl-terminated poly(ethylene glycol) oligomers (PEG, Mn= 600−2 000) to increase the water permeability of BPS-20. Unlike commercial state-of-the-art polyamide RO membranes, the blend materials do not degrade when exposed to aqueous chlorine (hypochlorite) at pH 4.
2006
1. UI (User Interface) in Product Design in Chemical Engineering and its Future Application in Ubiquitous Society with IT devices
Hee Jeung Oh, Jung Mi Park and Kyun Pyo Lee, The 19th International Symposium on Chemical Engineering Kyushu(Japan)-Daejeon/Chungnam(Korea), Kitakyushu, Japan, 2006